
Application controls – An Introduction (System Audit)
Introduction to Application Controls, Background on App controls – Testing, Overview and way forward.
Background
Auditors have to increasingly rely on Information Systems (popularly know as ERP). Coming from commerce, accounting, law and finance background, they cannot be expected to be well versed with Information System and it’s related technologies. Hence ISA comes into picture. Information System Auditors (ISA) possesses knowledge of Commerce, Information Systems and related technologies.
Auditors rely on the System Audit performed by IS Auditors and take comfort on the System they are using to Audit Financials and Books of Accounts. A classic example would be extracting of Trial Balance (TB) . When auditors extract TB, they assume that all the accounts are reflected in TB (i.e. completeness) and all the balances for every account which are reflected in TB are calculated considering all the accounting entries (i.e. correctness). The assumption of auditor will hold good as long as the System which auditor is using is audited by IS auditor and IS auditor has given the testing of the controls as Effective.
The work of the IS Auditor (i.e. Systems Auditor) with relation to giving reliance to Auditor on System / ERP predominantly means testing of Application Controls.
Definition
Application controls are controls over the input, processing, and output functions. From the 30,000 foot view they include things like:
Ensure the input data is complete, accurate and valid
Ensure the internal processing produces the expected results
Ensure the processing accomplishes the desired tasks
Ensure output reports are protected from disclosure
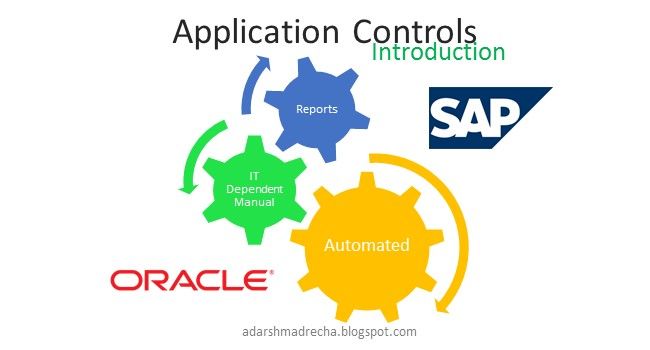
The Big 4 (Deloitte, EY, KPMG, PWC) have classified the application controls in following
- Automated control
- IT Dependent Manual control
- Manual control
- Reporting Testing (not exactly a control)
Big4 operates in 2 legal entity format, i.e. one legal entity in their own name and another (one or more) as a Audit Firm. (See Table below). The main entity undertakes IS Audit and Audit (Assurance) Entity undertakes Audit.
| Deloitte Deloitte Haskins & Sells, Deloitte Haskins & Sells LLP, P C Hansotia, C C Chokshi & Co, S.B. Billimoria, M.Pal & Co., Fraser & Ross and Touche Ross & co and A.F Ferguson, Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, Deloitte & Touche Consulting, Deloitte Audit & Enterprise Risk Services |
PWC Price Waterhouse, Price Waterhouse & Co., Lovelock & Lewes, and Dalal & Shah, PricewatershouseCoopers, PricewaterhouseCoopers Service Delivery Centre |
EY S.R.Batliboi & Co. LLP, S.R.Batliboi & Associates LLP, S.V.Ghatalia & Associates LLP, S R B C & CO LLP, Ernst & Young LLP, PDS Legal |
KPMG BSR & Co LLP, BSR & Associates LLP, BSR And Company, BSR & Co., BBSR and Co., BSSR & Co., BSR And Associates, Advaita Legal, SMA & Associates |
Legal entity information source : Wikipedia
Thus in the above working format, the – Automated control, IT Dependent Manual control, Reporting Testing are tested by ITRA (Information Technology Risk Assurance) Team and Manual controls are tested by Audit (i.e. Assurance) Team.
Testing Methodology
Having experience in IIC (Industrial, Infrastructure, Consumer) Team at EY, I will be covering the Application controls only from Manufacturing (Consumer Products, FMCG, Pharma, Lubricants, Fertilizers) point of view.
Testing methodology will vary (not significantly) on the system being audited. I classify ERP as below
- Extensively configurable and Open system (eg – SAP, MS Dynamix)
- Extensively Configurable but relatively closed (eg – Oracle, Sun System, Ariba, Taleo)
- Less Configurable (eg – Tally)
- Hard coded configuration (eg – Custom made ERP)
For Automated and IT Dependent
The testing for Automated control and IT Dependent Manual control is bifurcated in 2 parts
- Walk-through Testing
- Configuration
In walk-through Testing, we do a testing of ONE. Since ERP is after all a computer software, if it processes data in a particular format, it will continue to do so for any other same type of data. Hence test of ONE.
In Configuration Testing, we check configuration in the ERP in Extensively Configurable but relatively closed ERP and Obtain configuration data in Extensively configurable and Open system ERP.
This is just Tip of ice berg. We shall discuss each Application controls individually and dig deep, really deeeeeeeeppppp to understand what all tests has to be done.
So stay tuned for the next post on the blog. Don’t forget to subscribe, if you haven’t.













never learned about this but have not been able to understand, a little reading this article dala become more aware of the teachings of yesterday 🙂
Warm greetings from HBT
Thanks for sharing this wonderful post.